Difference between revisions of "Pretty Printers"
From Code::Blocks
GravityWe11 (talk | contribs) |
GravityWe11 (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
Links: | Links: | ||
[http://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Python-API.html GDB Python API] | [http://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Python-API.html GDB Python API] | ||
| + | |||
[http://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Pretty-Printing.html GDB Pretty Printing] | [http://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Pretty-Printing.html GDB Pretty Printing] | ||
===To Do=== | ===To Do=== | ||
The third column in the Codeblocks popup and watch window displays a long unformatted string. Codeblocks is calling the GDB whatis command. Can this command be Pretty-Printed? | The third column in the Codeblocks popup and watch window displays a long unformatted string. Codeblocks is calling the GDB whatis command. Can this command be Pretty-Printed? | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 25 October 2012
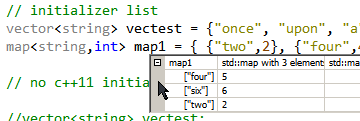
GDB Pretty Printers for STL output nicely formatted variables, even for vectors and maps. This works in GDB, and if enabled, in the hover pop-up and watch window in Code::Blocks.
Step 1 - Test with GDB
- Install a python-enabled GDB. For Windows, you can install MinGW-Builds over MinGW (consider backing up MinGW first). This updates GCC to 4.7.2 and includes a Python enabled GDB.
- Create a GDB Command File to enable the printer. Store in c:\mingw\bin\pp.gdb (or wherever you want). Here is a sample command file. Replace the path with your path to printers.py. NOTE: A Python STL printer.py is included with MinGW and MinGW-Builds, so there is no need to download one. It only needs to be turned on, which is the purpose of the command file
python
import os, sys
lib_path = os.path.abspath('c:/MinGW/share/gcc-4.7.0/python/libstdcxx/v6')
sys.path.append(lib_path)
#print 'path is [%s]' % ', '.join(map(str, sys.path))
from printers import register_libstdcxx_printers
register_libstdcxx_printers (None)
end
- Test
- Set a breakpoint in a program and debug
- Run GDB command file (can use Codeblocks debugger tab command, or GDB from console) (substitute your path if necessary)
(gdb) source c:\MinGW\bin\pp.gdb
- Test the printer - example:
(gdb) print words2
$1 = std::vector of length 3, capacity 4 = {"one", "two", "three"}
Step 2 - Add to Codeblocks
Once the printer works in GDB, there are two steps to activate in Codeblocks:
- Set debugger initialization command:
Codeblocks->Settings->Debugger->Default->Debugger initialization commands
source $(TARGET_COMPILER_DIR)bin\pp.gdb
- Comment out the Codeblocks gdb handler:
- Edit the file (path to Codeblocks)\share\CodeBlocks\scripts\gdb_types.script
- Add comments as follows:
/* STL String
driver.RegisterType(
_T("STL String"),
_T("[^[:alnum:]_]*string[^[:alnum:]_]*"),
_T("Evaluate_StlString"),
_T("Parse_StlString")
);*/
/* STL Vector
driver.RegisterType(
_T("STL Vector"),
_T("[^[:alnum:]_]*vector<.*"),
_T("Evaluate_StlVector"),
_T("Parse_StlVector")
); */
Other Info
Links: GDB Python API
To Do
The third column in the Codeblocks popup and watch window displays a long unformatted string. Codeblocks is calling the GDB whatis command. Can this command be Pretty-Printed?