Difference between revisions of "Pretty Printers"
GravityWe11 (talk | contribs) |
m (add a new stub for pretty printer for msys2) |
||
| (37 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | GDB Pretty Printers for STL | + | [[Category: User Documentation]] |
| + | GDB Pretty Printers for STL display nicely formatted variables in the hover pop-up and watch window, for all STL containers (vectors, maps, etc). | ||
---- | ---- | ||
[[File:Pprint1.png|border|Popup example]]<br> | [[File:Pprint1.png|border|Popup example]]<br> | ||
==Test with GDB== | ==Test with GDB== | ||
| − | * | + | *Ensure GDB is python-enabled. For Linux (tested with recent Ubuntu), it is enabled by default. For Windows, MinGW's GDB is not python enabled. One option is to install [http://sourceforge.net/projects/mingwbuilds/ MinGW-Builds] over MinGW (consider backing up MinGW first). This updates GCC to 4.7.2 and includes a Python enabled GDB. |
| − | *Create a GDB [http://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Command-Files.html Command File] to enable the printer. Store in c:\mingw\bin\pp.gdb (or | + | <ol> |
| + | To test, launch GDB from console: | ||
| + | <span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre> | ||
| + | (gdb) python print sys.version | ||
| + | </pre></span> | ||
| + | If python is enabled, the version will be printed (probably 2.7.x), otherwise, a message will indicate python scripting is not supported. | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | *Download printers.py (if necessary) | ||
| + | :Windows users with MinGW should already have this file in /MinGW/share/gcc-4.7.2/python/libstdcxx/v6. | ||
| + | :Linux users can download printers.py [http://gcc.gnu.org/svn/gcc/trunk/libstdc++-v3/python/libstdcxx/v6/printers.py here]. Save as <tt><span style="font-size: 10pt">/home/username/gdb_printers/printers.py</span></tt>. | ||
| + | *Create a GDB [http://sourceware.org/gdb/onlinedocs/gdb/Command-Files.html Command File] to enable the printer. Store in <tt><span style="font-size: 10pt">c:\mingw\bin\pp.gdb</span></tt> (windows) or <tt><span style="font-size: 10pt">/home/username/gdb_printers/pp.gdb</span></tt> (linux). Below is a sample command file. Replace the path c:/MinGW/share... with your path to printers.py. | ||
<blockquote><span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre> | <blockquote><span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre> | ||
python | python | ||
| − | import | + | import sys |
| − | + | sys.path.insert(0, 'c:/MinGW/share/gcc-4.7.2/python/libstdcxx/v6') | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
from printers import register_libstdcxx_printers | from printers import register_libstdcxx_printers | ||
register_libstdcxx_printers (None) | register_libstdcxx_printers (None) | ||
| Line 18: | Line 27: | ||
*Test | *Test | ||
#Set a breakpoint in a program and debug | #Set a breakpoint in a program and debug | ||
| − | #Run | + | #Run the command file from GDB (can use Codeblocks->debugger tab->command, or in GDB from the console) (substitute your path if necessary) |
<ol><span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre>(gdb) source c:\MinGW\bin\pp.gdb</pre></span></ol> | <ol><span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre>(gdb) source c:\MinGW\bin\pp.gdb</pre></span></ol> | ||
<ol start="3"> | <ol start="3"> | ||
| Line 28: | Line 37: | ||
==Add to Codeblocks== | ==Add to Codeblocks== | ||
| − | Once the | + | Once the command file is working correctly, there are two steps to activate in Codeblocks: |
| − | #Set debugger initialization command:<br/><span style="font-size: 10pt"><tt>Codeblocks->Settings->Debugger->Default->Debugger initialization commands</tt></span> | + | #Set debugger initialization command (substitute your path as necessary):<br/><span style="font-size: 10pt"><tt>Codeblocks->Settings->Debugger->Default->Debugger initialization commands</tt></span> |
| − | <ol><span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre>source | + | <ol><span style="font-size: 10pt"><pre>source c:\MinGW\bin\pp.gdb</pre></span> |
| + | NOTE: A bug in the Linux version of Codeblocks may prevent entering anything in the Debugger Initialization Commands field. A work-around is to open a CBP project file via a file manager, which in turn launches Codeblocks and seems to resolve the issue. | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
<ol start="2"> | <ol start="2"> | ||
| − | <li> | + | <li>Disable Codeblocks handling of watch values (needed only for versions older than 17.12):</li> |
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | + | <ol><span style="font-size: 10pt"><tt>Codeblocks->Settings->Debugger->Default->Enable Watch Scripts = Unchecked</tt></span></ol> | |
| − | |||
| − | <ol><span style="font-size: 10pt">< | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Other Info=== | ===Other Info=== | ||
Links: | Links: | ||
| Line 62: | Line 56: | ||
===To Do=== | ===To Do=== | ||
The third column in the Codeblocks popup and watch window displays a long unformatted string. Codeblocks is calling the GDB whatis command. Can this command be Pretty-Printed? | The third column in the Codeblocks popup and watch window displays a long unformatted string. Codeblocks is calling the GDB whatis command. Can this command be Pretty-Printed? | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==See also== | ||
| + | * [[Debugging with Code::Blocks]] | ||
| + | * [[Debugger scripts]] | ||
| + | * [[Configure GDB pretty printer for Msys2]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:36, 20 March 2021
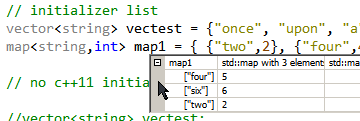
GDB Pretty Printers for STL display nicely formatted variables in the hover pop-up and watch window, for all STL containers (vectors, maps, etc).
Test with GDB
- Ensure GDB is python-enabled. For Linux (tested with recent Ubuntu), it is enabled by default. For Windows, MinGW's GDB is not python enabled. One option is to install MinGW-Builds over MinGW (consider backing up MinGW first). This updates GCC to 4.7.2 and includes a Python enabled GDB.
-
To test, launch GDB from console:
(gdb) python print sys.version
If python is enabled, the version will be printed (probably 2.7.x), otherwise, a message will indicate python scripting is not supported.
- Download printers.py (if necessary)
- Windows users with MinGW should already have this file in /MinGW/share/gcc-4.7.2/python/libstdcxx/v6.
- Linux users can download printers.py here. Save as /home/username/gdb_printers/printers.py.
- Create a GDB Command File to enable the printer. Store in c:\mingw\bin\pp.gdb (windows) or /home/username/gdb_printers/pp.gdb (linux). Below is a sample command file. Replace the path c:/MinGW/share... with your path to printers.py.
python import sys sys.path.insert(0, 'c:/MinGW/share/gcc-4.7.2/python/libstdcxx/v6') from printers import register_libstdcxx_printers register_libstdcxx_printers (None) end
- Test
- Set a breakpoint in a program and debug
- Run the command file from GDB (can use Codeblocks->debugger tab->command, or in GDB from the console) (substitute your path if necessary)
(gdb) source c:\MinGW\bin\pp.gdb
- Test the printer - example:
(gdb) print words2
$1 = std::vector of length 3, capacity 4 = {"one", "two", "three"}
Add to Codeblocks
Once the command file is working correctly, there are two steps to activate in Codeblocks:
- Set debugger initialization command (substitute your path as necessary):
Codeblocks->Settings->Debugger->Default->Debugger initialization commands
source c:\MinGW\bin\pp.gdb
NOTE: A bug in the Linux version of Codeblocks may prevent entering anything in the Debugger Initialization Commands field. A work-around is to open a CBP project file via a file manager, which in turn launches Codeblocks and seems to resolve the issue.
- Disable Codeblocks handling of watch values (needed only for versions older than 17.12):
- Codeblocks->Settings->Debugger->Default->Enable Watch Scripts = Unchecked
Other Info
Links:
To Do
The third column in the Codeblocks popup and watch window displays a long unformatted string. Codeblocks is calling the GDB whatis command. Can this command be Pretty-Printed?