Difference between revisions of "Debugging with Code::Blocks"
m (add category) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[Category: User Documentation]] | ||
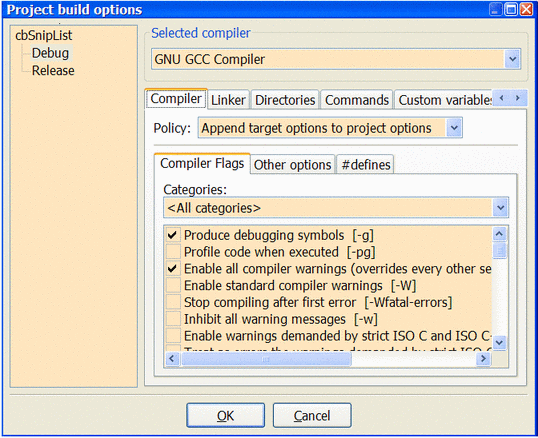
Make sure that the project is compiled with the -g compiler option. This ensures that the executable has debug symbols included. | Make sure that the project is compiled with the -g compiler option. This ensures that the executable has debug symbols included. | ||
Revision as of 19:45, 10 November 2006
Make sure that the project is compiled with the -g compiler option. This ensures that the executable has debug symbols included.
Keep in mind that you may have to re-build your project as up-to-date object files might not be re-compiled with -g otherwise. Please be aware that in compilers other than GCC, -g might be a different switch.
Menu => Project => Build Options
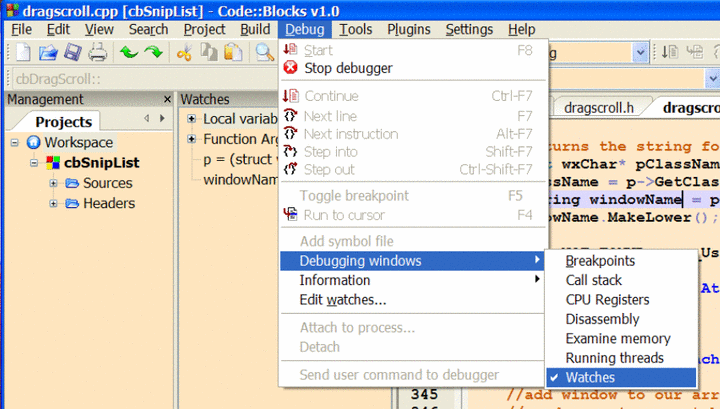
Open The Debugger Watches Window
Find the line containing the variable to be watched. Set a breakpoint in a position that will allow you to observe the variable value.
Menu => Debug => Toggle Breakpoint
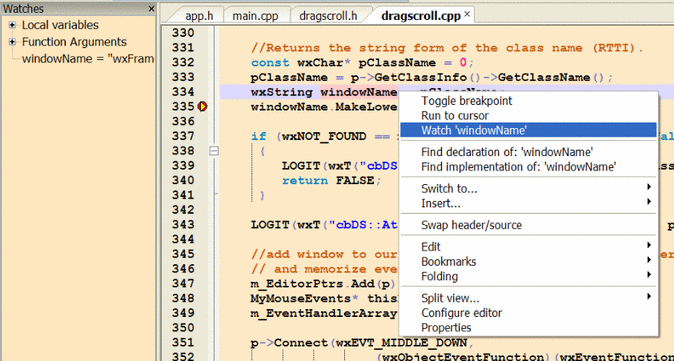
Run the debugger until the breakpoint is reached. Right click the variable to set a watch in the Watch Window.
Notes:
Breakpoints may also be toggled with a left click in the left editor margin.
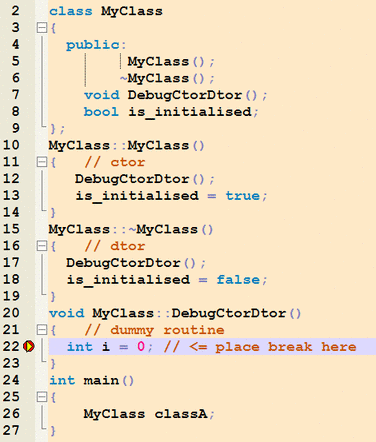
Breakpoints do not work in constructors or destructors. They do, however, work in routines called from them. This is a GDB restriction, not a bug. So you could do something like:
...and place a breakpoint in "DebugCtorDtor" at the line "int i = 0;" . The debugger will break at that line. If you then step the debugger (Menu Debug => Next Line; or alternatively F7) you'll reach the code in the contructor/destructor ("is_initialised = true/false;").
Last edited: MortenMacFly 02:52, 26 October 2006 (EDT)