Code Completion Design
How to build
Get the source code
When you download the svn source code of code::blocks,(see here Installing_Code::Blocks_from_source_on_Windows#Code::Blocks_sources the source code of CodeCompletion plugin was already included.
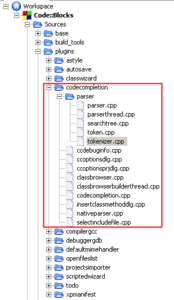
See a screen shot of these code opened in code::blocks under windows below.
Build the code completion plug in
Note, you should use "update.bat" to copy the new generated dll to the destination and strip the debug information. Here is the modified bat file which only update CodeCompletion.DLL.
@echo off setlocal echo Creating output directory tree set CB_DEVEL_RESDIR=devel\share\CodeBlocks set CB_OUTPUT_RESDIR=output\share\CodeBlocks set ZIPCMD=zip xcopy /D /y %CB_DEVEL_RESDIR%\plugins\codecompletion.dll %CB_OUTPUT_RESDIR%\plugins\codecompletion.dll echo Stripping debug info from output tree strip %CB_OUTPUT_RESDIR%\plugins\codecompletion.dll
see Installing_Code::Blocks_from_source_on_Windows for more information.
Low level parser(Lexical analysis)
For someone haven't heard what does "Token" and "Tokenize" means, you should read the wikibooks article A brief explain of what does a parser do and Tokenize on wikipedia. Shortly, a parser treats your C++ or C code as a large array of characters, then this big string was divided to small atom strings(such as symbols, identifiers, keywords, digital numbers), meanwhile "spaces" and "comments" were ignored.
for a simple c++ program like below
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
After tokenizing, it should give these 15 tokens
1 = string "int" 2 = string "main" 3 = opening parenthesis 4 = closing parenthesis 5 = opening brace 6 = string "std" 7 = namespace operator 8 = string "cout" 9 = << operator 10 = string ""hello world"" 11 = string "endl" 12 = semicolon 13 = string "return" 14 = number 0 15 = closing brace
Tokenizer class
A class named "Tokenizer" was introduced in "tokenizer.cpp" and "tokenizer.cpp". There are several steps to running the Tokenizer class.
parser thread
A thread must be created to parse a source file. see parserthread.cpp and parserthread.h
Read a source file
Open the source file and convert the file buff to Unicode mode.(since we are all using Unicode build of code::blocks, and ANSI mode is outdated).
Get or Peek a token
The class contains a Pointer to the current position of the character(m_TokenIndex), you can Get or Peek to get the correct token you desired.
//Get the current Token and increase the Tokenindex wxString GetToken(); //Peak the current and NOT increase the index wxString PeekToken();
For example, if the Tokenizer was parsing the example code above.
- After initialize the Tokenizer, call the GetToken() function will return a wxString "int" and increase the token index to pointing to "int".
- Then, call the PeekToken() will return a wxString "main", but the tokenindex was still pointing to "main".
- If you call the GetToken() again, then it will return a "main" immediately and increase the file pointer to "main".
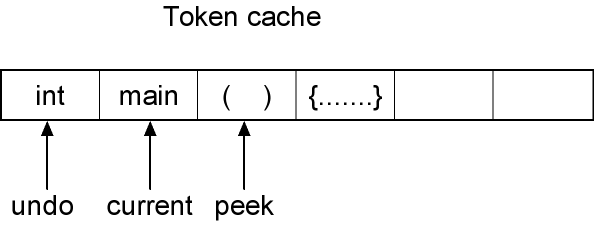
Note: Internally, the Tokenizer class use a "undo and peek cache" to do this trick. Once a token is peeked, it will be saved in the m_Peek member, so, calling GetToken() will quickly return saved value without calling the "DoGetToken()" procedure again.
Nested Value
This value was keep to indicate your are in the correct brace pair.If the Tokenizer meets a {, it will increase the nestValue, and if it meets a }, it will decrease the m_NestLeve. See the pseudo code in Tokenizer.cpp below.
if (CurrentChar() == '{')
++m_NestLevel;
else if (CurrentChar() == '}')
--m_NestLevel;
SkipUnwanted tokens
There is a member function in Tokenizer class to skip comments, assignments, preprocessor etc.
For example, if there is a statement below:
a = b + c;
if SkipUnwanted() meet the "=" symbol, it will skip everything until it meets "," or ";" or "}", this means this statement will be omitted by the Tokenizer if m_SkipUnwantedTokens == true.
Sometimes, this behavior becomes a nightmare to parse the statement like default argument in template.
template<class T = int>
class abc {
T m_a;
......
......
}
if the Tokenizer find that a "=", it will skip any characters until it meets a "}", so, the class declaration will totally be skipped. So, at this time, we should manually disable this functionality by setting m_SkipUnwantedTokens = false to parse these statements correctly. That's why you will see many situations when you enter a function, you should save the m_SkipUnwantedTokens and disabled it, when you leave a function, you should manually restore it.(Seefunction implementation in ParseThread.cpp)
Return a correct token
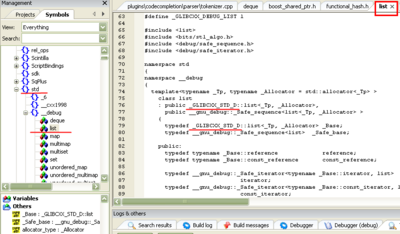
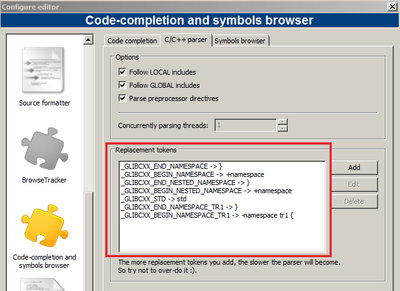
Special token should be replaced for parsing correctly. For example, in the standard c++ header (mingw), there are a string named "_GLIBCXX_STD", this should be replaced to "std". See the dialog below.
The inline function in the Tokenizer class will check whether a token should be replaced before return.
//This is a map, check the first string and return the second string
inline const wxString& ThisOrReplacement(const wxString& str) const
{
ConfigManagerContainer::StringToStringMap::const_iterator it = s_Replacements.find(str);
if (it != s_Replacements.end())
return it->second;
return str;
}
Setting the replacement mapping. Note that before return a token, a replacement map was searched to check if it matches any entry in the map, so, the bigger this map goes, the slower it will do parsing.
Note: CodeCompletion plugin is not a preprocessor, so it is difficult to deal with the source mixed with many macro, or some strange marcos. This is something like Ctags' replacement options "−I identifier−list" in ctags option detial or CodeCompletion macro FAQ
High level parser(Syntax Analysis)
Basically, we can say, the low level parser(Tokenizer) moves its pointer character by character, and return a wxString(token) to feed the high level parser(Syntax analyzer). A Token(note: it as a capital means it's class type) class was introduced to describe its character.
Token class
For boosting the speed of allocating Tokens, the "new" and "delete" operator were overloaded in its base class BlockAllocated. See the memory pool page on wikipedia as a reference.
class Token : public BlockAllocated<Token, 10000>
{
......
wxString m_Type; // this is the return value (if any): e.g. const wxString&
wxString m_ActualType; // this is what the parser believes is the actual return value: e.g. wxString
wxString m_Name;
wxString m_Args;
wxString m_AncestorsString; // all ancestors comma-separated list
unsigned int m_File;
unsigned int m_Line;
unsigned int m_ImplFile;
unsigned int m_ImplLine; // where the token was met
unsigned int m_ImplLineStart; // if token is impl, opening brace line
unsigned int m_ImplLineEnd; // if token is impl, closing brace line
TokenScope m_Scope;
TokenKind m_TokenKind;
bool m_IsOperator;
bool m_IsLocal; // found in a local file?
bool m_IsTemp; // if true, the tree deletes it in FreeTemporaries()
bool m_IsConst; // the member method is const (yes/no)
int m_ParentIndex;
TokenIdxSet m_Children;
TokenIdxSet m_Ancestors;
TokenIdxSet m_DirectAncestors;
TokenIdxSet m_Descendants;
......
};
Basically, you can see the Token class contains the information for locating. For example, in the previous source code. A Token for "main" should contains it's name (obviously , m_Name="main" ), then m_File will record which file dose this Token exist. m_Line will give the line number of "main" in this source file, and so on.
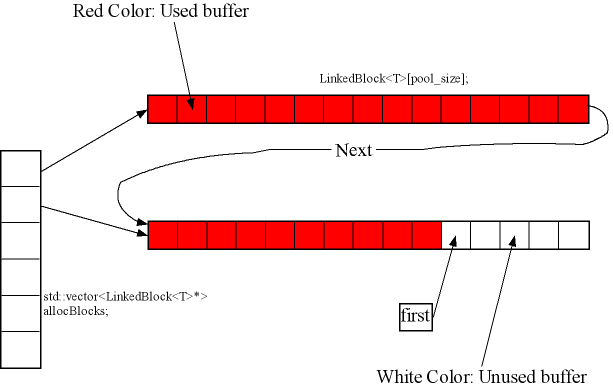
BlockAllocated class
In BlockAllocated class, there is only a static member say "static BlockAllocator<T, pool_size, debug> allocator;" to keep all the pre-allocated memory for all derived class.
10000 means a pool of 10000 Tokens were allocated in the memory pool, so, dynamically allocate a Token object will be fast and efficient.
ParserThread
The function Parse() will do the most job of syntax analysis. See the pseudo code below.
ParserThread::Parse()
{
......
do
{
......
DoParse();
......
}while(false);
return result;
}
In the DoParse(), it checks the token from Tokenizer. For example, if the token words = "enum", then, the ParserThread::HandleEnum() will do the job to parse this enum block.
TokenTree&SearchTree
When a specific Token is identified( whether it's a global variable, a class declaration, a class member function, and so on), it will be recorded in a database(TokenTree), also, for fast string matching, a compact Patricia tree(see the wikipedia Patricia tree on wikipedia) is build to keep their names.
For example, If you add three item to the TokenTree.
mytree->AddItem(_T("physics"),_T("1 - uno"));
mytree->AddItem(_T("physiology"),_T("2 - dos"));
mytree->AddItem(_T("psychic"),_T("3 - tres"));
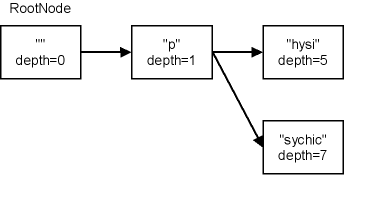
The Tree structure will show as
- "" (0)
\- "p" (4)
+- "hysi" (2)
| +- "cs" (1)
| \- "ology" (3)
\- "sychic" (5)
Search Tree Node Depth
Depth of Search Tree Node is defined by the string length from the root tree. See a depth of each node on the search tree below. For example, the Node of "hysi" has a m_Depth = 5 ("" + "p" + "hysi" = 5).
Search Tree Node Lable
For example, the node ""hysi" (2) has two children, they are "cs" (1) and "ology" (3), show below.
For more information, see the forum discussion here. [/index.php/topic,1696.0.html rickg22's SearchTree development] as a reference.
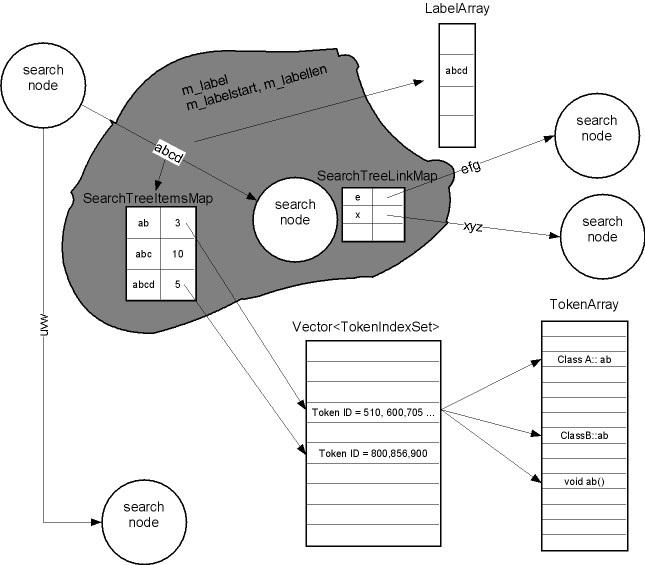
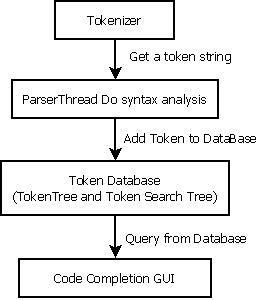
flow of Token
This the a belief view of the Token flow chart. The parser collect the token information, and record them in the TokenSearchTree, the GUI function can query words from the database to show function tips or do a convenient navigation.
UI issue
Debug Log output
If you want to debug your plug-in, you may need to Logout the debug information. Mostly, here is the code
Manager::Get()->GetLogManager()->DebugLog(_("XXXXX "));
Also, you need start the codeblocks with the command line argument. For example in windows.
codeblocks.exe --debug-log
then a Code::blocks debug panel will be shown to display the log.
Usefull Links
- A discussion on search tree in the forum [/index.php/topic,1696.0.html] and [/index.php/topic,1581.0.html].
- Another opensource IDE VCF builderorvcfbuilder on sf, By the way , VCF use a CodeStore based on antlr parser to deal with parsing, the whole source code can be check out from
svn co https://vcfbuilder.svn.sourceforge.net/svnroot/vcfbuilder vcfbuilder
- online bookData Structures and Algorithms II Course and pdf lectures
- A forum discussion on why a standard perprocessor and parser works slowly. [/index.php/topic,2494.msg19801.html#msg19801 parsing iostream header takes 5 seconds]
- CodeLite is another open source IDE, it use a simple c++ parser generated from Lex and Yacc tools.