WxSmith tutorial: Hello world
"Hello world" Tutorial
THIS TUTORIAL IS UNDER RECONSTRUCTION BEGINNING 2012 MARCH 1. CHECK BACK IN A FEW DAYS FOR AN UPDATED AND EXTENDED VERSION. MEANWHILE, UNTIL THIS MESSAGE DISAPPEARS, YOU WILL FIND SOME BREAKS AND INCONSISTENCIES. IT SHOULD BE GOOD DOWN TO THE LINE "END OF CURRENT EDITING".
In this first tutorial, we will use wxSmith to put the words "Hello, World!" on the screen. Ever since the appearance of The C Programming Language in 1978, writing such a program has been the traditional first step in learning nearly every computer language.
Before we start, you must either compile wxWidgets or download precompiled binaries and header files. These steps are described on the wiki pages mentioned here:
- Windows users should see the wiki page:Compiling wxWidgets 2.6.2 to develop Code::Blocks (MSW) or Installing Code::Blocks from source on Windowsor WxWindowsQuickRef. There are two ways to install the wxWidgets libraries, You can download the wxWidgets source and compile it yourself, or you can download the wxPack from [1] and install it. The wxPack contains a pre-compiled wxWidgets library, so you can save a lot of time by that route. Ubuntu Linux users can install it from the Ubuntu repositories.
We will assume that you have wxWidgets ready and working with Code::Blocks. You should probably create a directory with a name something like CBProjects for saving your work on these tutorials. Each tutorial will be a separate "project" and will occupy a file in this directory.
After downloading and installing Code::Blocks, double-click its icon on the desktop to start it. Here is the Code::Blocks opening window:
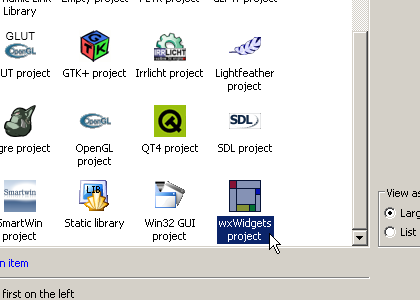
On the main menu, Click File | New | Project ... and then find and click the wxWidgets Project icon, pointed to by the cursor in the screenshot below.
The next screen is a "Welcome" screen. Unless you just enjoy being welcomed by the program, you will check the box which eliminates it on future startups.
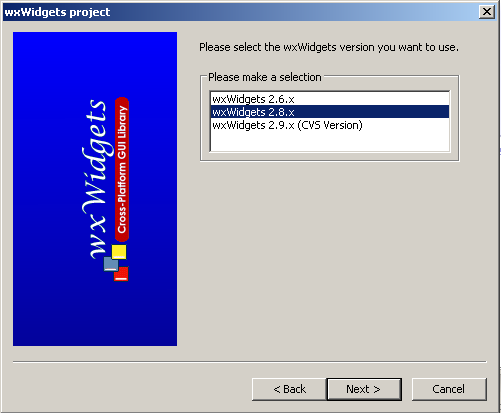
The next screen looks like this:
Select wxWidgets 2.8x and click the "Next >" button at the bottom of the screen.
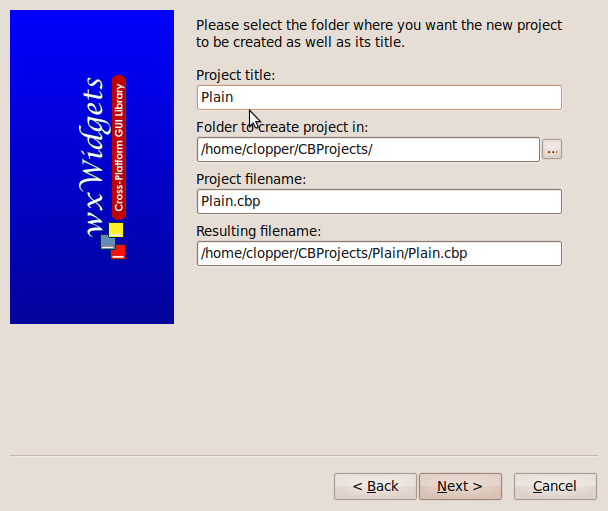
That brings you to the window where you specify the Project title and folder where you want to save the project. Other fields are then filled automatically. I chose “Plain” as the Project title and the other fields then adjusted to look like this:
Then click the “Next >” button at the bottom.
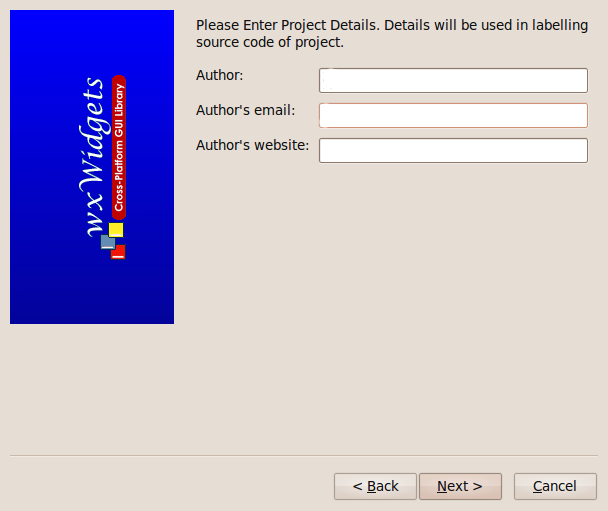
The next screen, shown below, allows you to mark your work with your identity. Fill in what you wish.
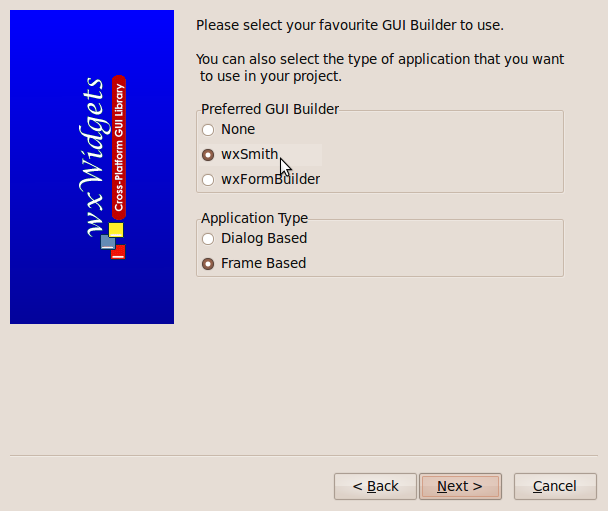
That brings up the window for choosing the GUI builder you wante to use, wxSmith or FormBuilder. We choose, of course, wxSmith.
Click the "Next" button at the bottom.
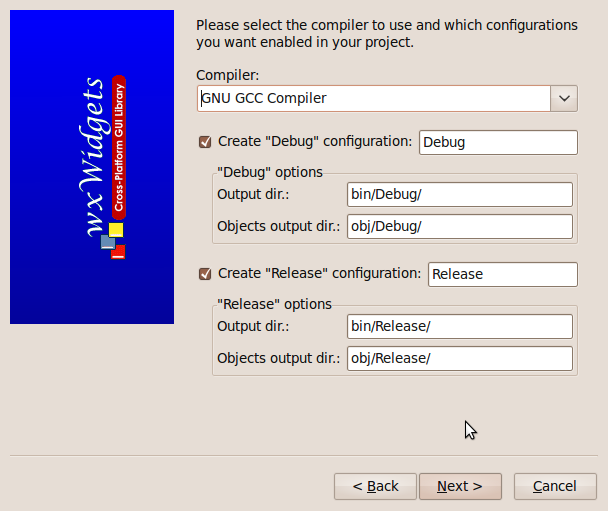
The next screen specifies what C++ compiler we want to use and whether we want a debug build (with extra code for debugging) or a smaller release build for use by others. We will go for the GNU CPP compiler and both build options, to be put in separate subfolders.
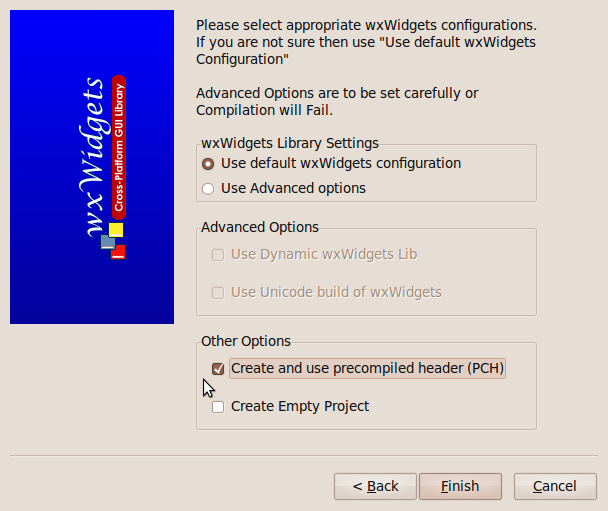
The final screen of this sort asks whether we want to use the standard, default, configuration or to use Advanced options. We will take the default. But, at the bottom, we choose to “Create and use precompiled headers, which speed up compilations after the first.
On the form where we chose the directory for saving the project, we chose a real directory, but that choice may lead to problems when you want to compile your project on other computers. Another choice is to use the Global Variable system. To open the dialog below or modify or change this global variable, you should click on the Code::Blocks main menu item Settings | Global variables. That brings up the Global Variables Editor.
When you use it, the location of the wxWidgets library is read from the variable you supply. This means that the location of the wxWidgets directory is not hard-coded inside your project, but is stored inside the global configuration of Code::Blocks. When your project is opened on a different computer, it will use that comoputer's configuration. The easiest option to use this global variable is to leave $(#wx) which means to use the global variable named wx. This name is reserved for wxWidgets and should be chosen in most cases.
When you use the global variable for the first time, it will ask for the wxWidgets directory. The only thing you need to do here is to enter a valid location in base field. This is required only for the first time since Code::Blocks will automatically use this setting for other projects you create.
Overview of the Interactive Development Environment (IDE)
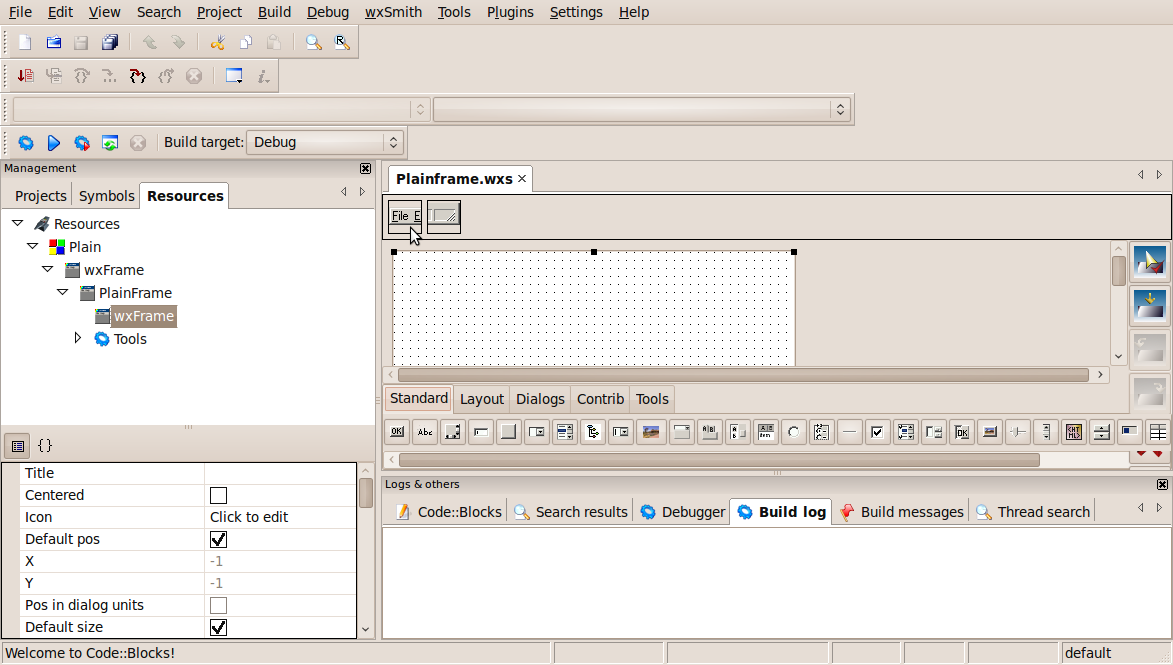
At the end of this preliminary sequence of forms we come to the Code::Blocks main IDE window. It should look something like this:
In the middle of the right side of the window, under the word “Plainframe.wxs”, is a panel with two square icons on the left; the one on the left brings up the menu bar editor while the one on the right brings up the status bar editor. We will return to the menu bar editor in the next tutorial. Below this panel and looking like a field of dots is the Editor window, where we will see both the GUI forms which we build and the C++ code we write. In the lower left corner of the whole window is the Properties/Events window, which will allow us to set properties of the component we are working on or to pick events, such as “OnClick” , to which we need to respond. To show properties, click on the left icon; to show events, click on the right icon marked {} to suggest C++ code.
Above the Properties/Events window is the Management window with three tabs, Projects, Symbols, and Resources. If all three tabs are not visible, drag the right border of the window to the right to reveal all three. (A “resource” in wxSmith parlance usually means a “form” or "window".) Above the Management window is a panel with several small but useful icons to
- Build the program, or
- Run it, or
- Build and run it, or
- Rebuild it, or
- Abort it.
When you run the cursor over them, the tool tips will tell you which is which.
Now look back to the Editor window. First of all, note that the window can be configured to use different colors,fonts and font sizes. Click "Settings ..." on the Code::Blocks main menu, and then "Editor". The screens are more or less self-explanatory.
Now back to the Editor window. Across the top you see three black square called drag handles. They have been set to cover a space larger than can be seen, but scrolling down reveals the whole field.
As an experienced programmer, you know there has got to be some code somewhere but you don't see it. To reveal it, double left click in the field of dots. Presto, there is the C++ code, and the *PlainMain.cpp tab has appeared above it. Clicking back on the Plainframe.wxs should return you to the view of the form, still the field of dots. (Again, it is important to have CB 10.04 or later.) In fact, we still have not seen all of the code. In particular, you will search in vain for the all-important OnInit() routine that starts the program. You can find it, however, by clicking Search | Find in Files and searching for OnInit with the scope of the search set to be “Project files”. The search finds it, sure enough, in PlainApp.cpp and opens this module in the Editor window.
We don't need OnInit right now, but we do need to make a change in PlainMain.cpp. Click on it in the bar above the editor, and its code appears in the editor.
Sometimes a program has a lot to do when the user clicks the close icon in the program's title bar, so wxSmith generates a frame for writing the code for those actions but it provides no code. Consequently, if we ran our program just as initially written by wxSmith, we won't be able to close it by just clicking that icon. To fix that inconvenient problem, find the spot in the code with these lines:
void PlainFrame::OnClose(wxCloseEvent& event)
{
}
Add the call to the Close() function so that the spot looks like this:
void PlainFrame::OnClose(wxCloseEvent& event)
{
Close();
}
Remember to make this change immediately whenever you start a new project.
You can now build and run this super-simple program. To do so, you can do any one of three equivalent things:
- in the top menu bar, click Build | Build and run.
- find and click the icon that looks like a right-pointing triangle in front of a cogwheel. Hovering the mouse pointer over it will show the tool tip “Build and run”.
- tap the F9 key.
If all goes well, you will see a window come up with a menu of two items: “File” and “Help”. Try the “Help” menu item first. Then you can use “File | Quit” or the exit icon on the title bar to exit the program.
If you are using Ubuntu and get no main menu bar when you run this program, you have fallen victim to Ubuntu bug 662077. Beginning with release 10.10, Ubuntu releases have had a bug causing programs built with wxSmith to fail to show their main menu bar. If this bug affects you, you may want to uninstall appmenu-gtk. You do that by clicking Applications | Software Sources, then using the search window to find appmenu-gtk. Clicking on it will allow you to choose to remove it.
Well, so far we have a program that runs and quits, but it does not yet display "Hello, World!". That's next.
Hello, World!
We now turn to the classic first program, namely getting the words “Hello, World!” onto the screen. The text could be added directly into the frame, as in GUI designers for a single operating sytem; but we need to learn to use sizers for cross-platform programming. What are sizers?
If you have been working with Java or Qt, you may remember something called Layout managers. The implementation in wxWidgets differs a little but does almost the same thing.
When adding components into windows you must somehow specify their position and size. wxWidgets tries to automate this process, and it uses sizers to do so. They automatically position and size window components, and they can also set the size of the window so that everything fits inside.
Sizers have one big advantage over direct placement of components. When you write cross-platform applications, you cannot assume that fonts, buttons, and so on have the same size on different operating systems. This problem can even occur on the same platform when using different window themes. When you use sizers, you don't have to worry about those problems. All sizing and placement is done automatically. Moreover, sizers can even reposition and resize window components when the main window changes size.
With that background, let's get started. When you look at the wxSmith editor, you'll notice that the area of the window is surrounded by eight black boxes or drag handles.
These drag handles surround the currently selected item. In our case it's a whole window. Adding new components to the window is simply done by clicking on one of the buttons in the palette at the bottom of the editor and then clicking somewhere on the resource. As you can see here,
when you keep your mouse cursor over a component in the palette, it will show its name. That may help you find components until you become familiar with their icons.
Let's add a new wxPanel component to our window - this is the fourth icon from the left. You will see that when you click the wxPanel item and then move the cursor over the resource, some part of the editor will change color. That's intentional and is used to show onto which part of the window the new item will be added.
After the wxPanel is ready, you will notice that the background color of the window changed to light gray. Now our window will look much more like other windows. Note that currently the selection changed to the added panel but since its size is equal to the frame's, it's hard to find out what's really selected. To make sure that wxPanel is selected, click somewhere on the light gray area of our window (Note to Linux users: wxFrame and wxPanel usually have the same background so it may look like nothing has changed; you may ensure that there's a wxPanel by looking into the resource browser).
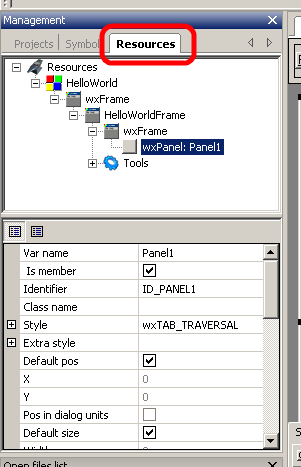
If you want to see the selection exactly or select items that overlap, you can use the resource browser. To show it, click on the resources tab located in the same place where the project browser is:
The resource tab consists of two parts. The first is the resource tree which shows the structure of your resources and the second one is the property browser which is common in GUI designers. Inside the resource tree you can find the currently selected item. In our case it is the wxPanel class we added before. The selected item also shows the name of this item: Panel1. This name is basically the variable which can be used to access this component in your code.
We added a new component by selecting the place for it. This is wxSmith's default behavior. However, there is another mode of adding items. In this mode, the new item is added right after you click on the palette's button. The position of the new item is relative to the current selection - just like a cursor in text editors. Basically we can add new items into three different positions relative to the selection:
- Before the selected widget
- After the selected widget
- Into the selected widget.
This can be changed by clicking one of four "placement" buttons on the right side of the editor:
The uppermost is the mode we used - "point by mouse". The next one means "add into", followed by "add before", and the last one means "add after". The current mode is show by a red check mark on the button.
Sometimes a few selection modes are disabled. This means that they are not valid for the currently selected item. For example you cannot add any comoponent into the wxButton component since wxWidgets declares it as one that cannot have child components. And when the main component (the window) is selected, you won't be able to add anything after it or before it.
Now let's assume that we've made a mistake and want to delete an item that we have just added. In fact we have a small mistake and will have to delete wxPanel. To this, click on the red X button:
When you click this button, it deletes the current selection, so if the panel didn't disappear, make sure it's selected and click the button again. Now we should have returned to the state at the beginning.
The mistake made here is that we've added wxPanel directly into the main frame. But as I've said before, we will be using sizers to manage the window's content. To use sizers, first we have to add a sizer into the main frame and then add wxPanel into it.
Sizers are available in the Layout tab on the palette. Switch to it and select wxBoxSizer:
This sizer tries to position items in one line, either horizontal or vertical. Horizontal is by default and we will use this.
After adding sizer, two things have changed. First is that our window now has a red border. This means that there's a sizer attached to it. When you look into the resource browser you will also see that the sizer has been added (you may need to click on the editor area to refresh the selection on the resource browser). The second thing is that the size of the window has shrunk to a small box. That's correct since the sizer is also responsible for resizing items.
Now let's add wxPanel. Make sure that we will add it into the sizer, not the main frame. After we do this, you will see something like this:
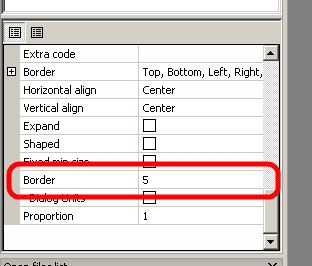
Here we can see our panel surrounded by drag boxes. There's also some dark gray border around it (it won't be visible on Linux). Each item added into the sizer can be surrounded by such a border. It's useful when you want to have spacing between items. But in our case we should get rid of it to get a more proper window. To do so, we will have to change a property inside the property browser. Search for border size and change it to 0:
Now when we have our panel adjusted, we can finally add the "Hello world" text. Since we will also use sizers to manage items added into wxPanel, we have to repeat the addition of wxBoxSizer into wxPanel. After the sizer is in its place, switch back into the Standard tab on the palette and add wxStaticText:
Because this text looks so lonely, let's add a button next to it by clicking on wxButton. Note that if you still have the "point by mouse" insertion mode turned on, half of the wxStaticText item will be coloured in light blue when you put the mouse over it. This is a hint for you: when the left half of the text is highlighted, the new item will be added before it, and when the right half is highlighted, it will be added after the text. So let's add the button after the text.
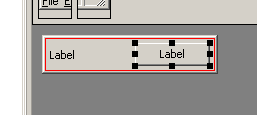
Now we should have this content:
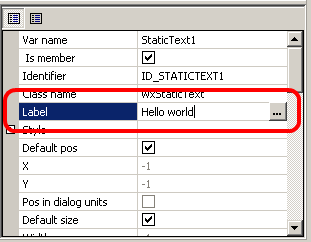
Now let's finally set our "Hello world" text. The wxStaticText control which we added before has the text "Label" on it. It is the default text set to all newly created wxStaticText classes. We will change it using the property browser similarly to changing the border size in the wxPanel class. To do it select our text first, find the Label property and change it to "Hello world":
You can also set multi line text by clicking on the "..." button or putting "\n" inside text (just like in c strings).
Let's react - making close button
Now let's do something with the button. Since buttons usually react when somebody clicks them, let's make it close the window. First thing we should do is to change text shown on button to notify user about function assigned to it. It is done just like in case of text - select button, find "Label" property and set it to "Close" (or anything you want ;) ).
Second thing is to assign event handler to this button. Basically event handlers are function which are called when some "event" occurs. In our case instead of "event" we could say "click on button" because that we want to process. As many GUI designer, wxSmith can automatically generate such handlers. They are accessed through property browser just like other properties. To switch to events you have to click second icon at the top of property browser (don't worry, those icons are going to change to something more self-explanatory):
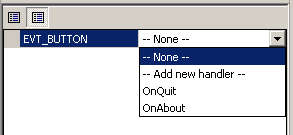
After you click on this icon, you will see all events supported by currently selected item. wxButton class support only EVT_BUTTON event so only this one is shown. When you click on this event and expand combo box you will see available options and handlers for this event:
When you select -- None -- there won't be handler function automatically assigned to this event (it may always be set manually), selecting -- Add new handler -- will generate new handler function. Below are shown other event handlers known to wxSmith which can be assigned to this event. We can see here OnQuit and OnAbout. Those handlers were created by wizard. So let's create new handler. We could use one of those defined, but since we haven't looked into source code yet, we don't know what they do. After you select new handler option, you will be asked for name of handler. This is simply name of function which will be called as a reaction for event.
When you enter new handler name, wxSmith will generate new handler function, open file with proper source code and put cursor inside handler function (note that you may need to press up or down cursor to show the line with cursor). Note that this function is member of class called for example HelloWorldFrame. wxSmith creates one such class for each resource. Since event handler function is member of this class, you have access to all the window from it. So when we want to close our window we just call Close function:
After compiling our project it will show our "Hello world" and "Close" button.
This is end of this tutorial, I hope that it showed some basics of wxSmith. If you have any problems with it or think that some parts are unclear, please contact me (byo) on forum.